> 개요
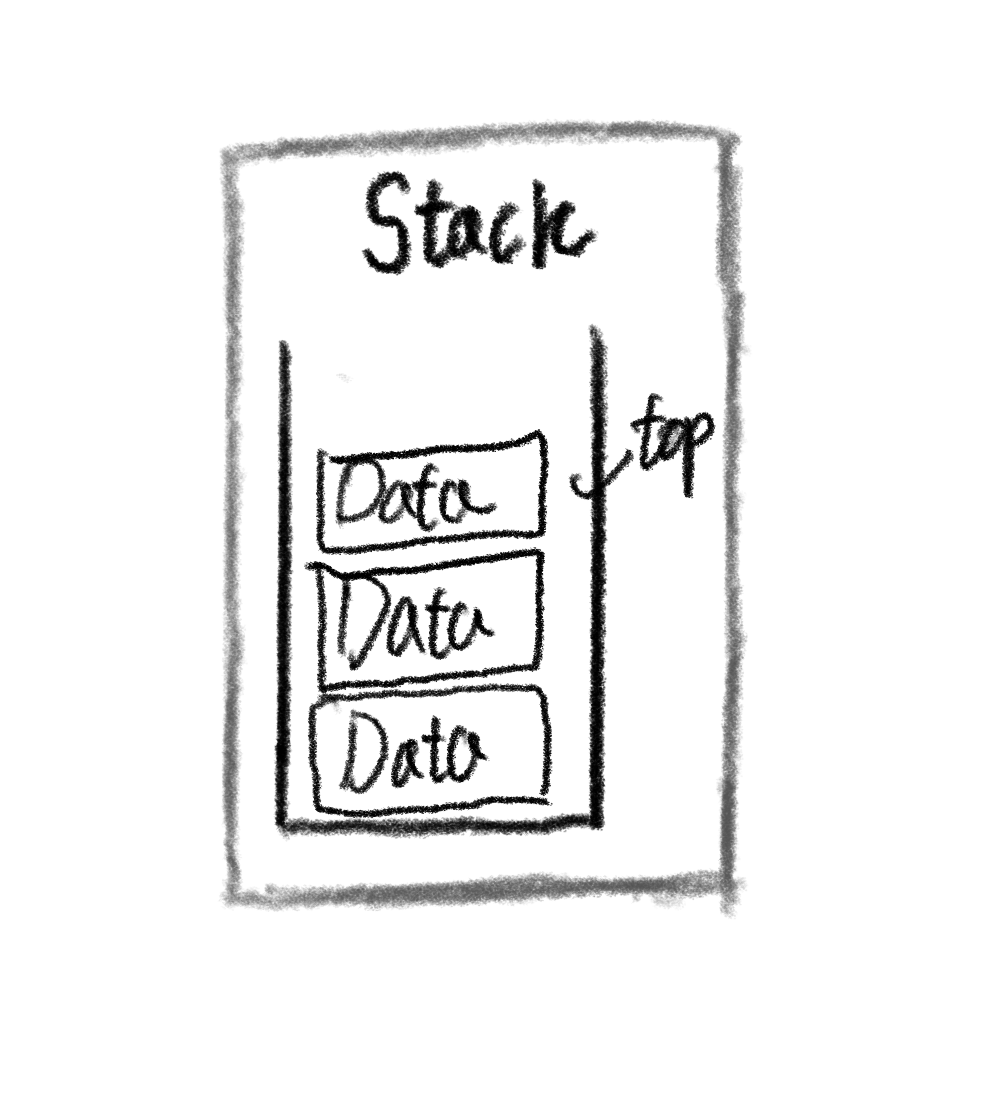
- ‘쌓다’ 라는 사전적 의미
- 후입선출 ( LIFO: Last In First Out )
- 가장 최근에 스택에 추가한 데이터가 먼저 제거됩니다.
- 활용 사례
- 웹 브라우저 - 뒤로가기
- 실행 취소 ( undo )
- 후위 표기법 등
> 사용법
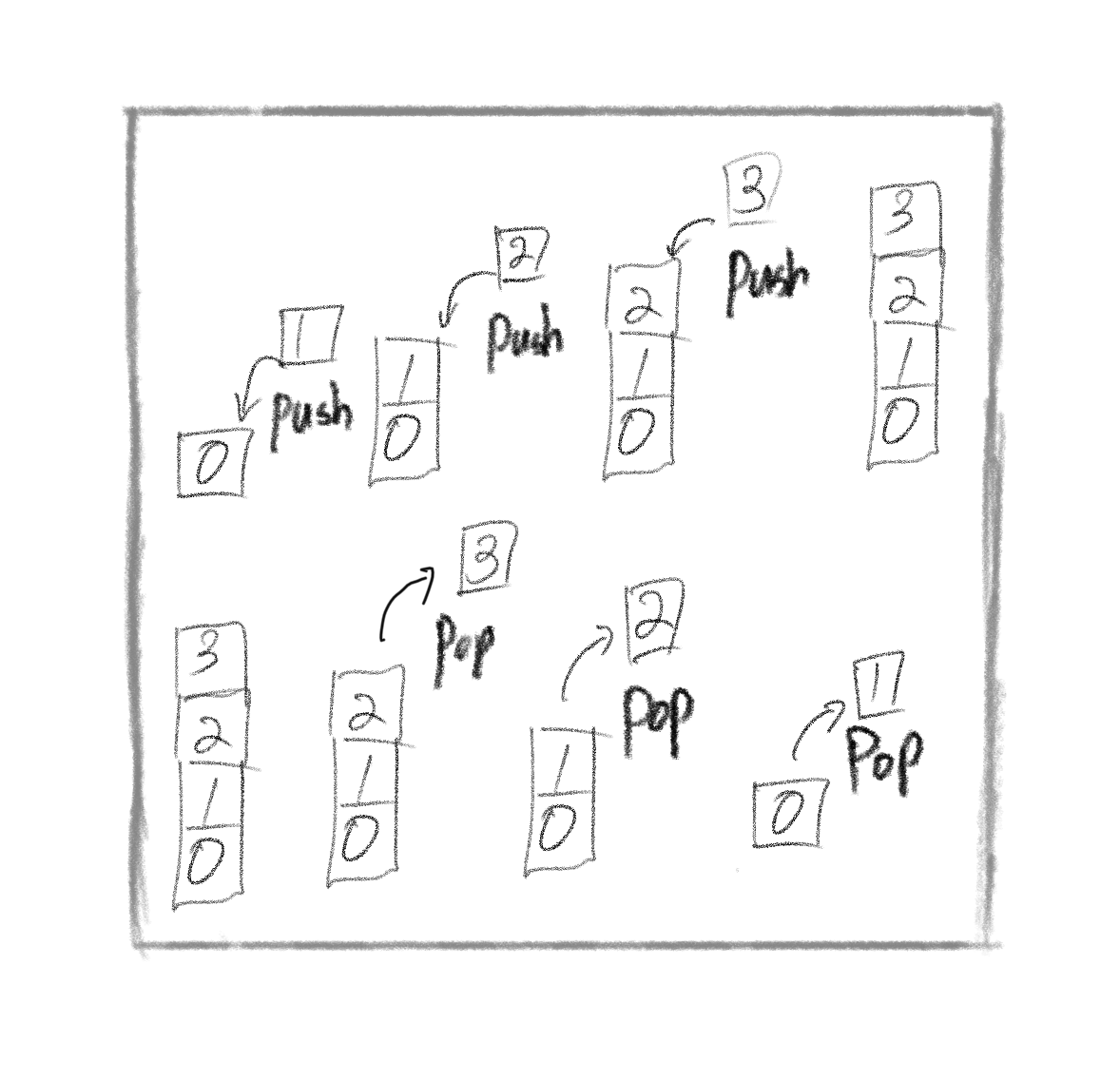
- 연산
- 삽입 - Push(item)
- 새로운 데이터를 스택(Stack)에 삽입한다.
- Top 값이 1 증가 후, 새로운 데이터를 삽입.
- 삭제 - Pop()
- 스택(Stack)에서 Top이 가르키고 있는 데이터를 삭제한다.
- Top 값이 1 감소.
- 읽기 - Peek()
- 스택(Stack)에서 Top이 가르키고 있는 데이터를 읽는다.
- Top 값의 변화 없음.
> 구현
구현방법은 배열(Array) 과 연결리스트(LinkedList) 방법이 있습니다.
모두 장단점이 있는데,
- 배열
- 구현이 쉽고, 데이터 접근속도가 빠르다.
- 하지만, 최대 데이터 수를 미리 지정해야 한다.
- 연결 리스트
- 현재 스택에 저장되어있는 자료 만큼 메모리를 잡아먹기 때문에 메모리 절감.
- 배열(Array) 구현
public class Stack {
private int top;
private int maxSize;
private Object[] stack;
public Stack(int maxSize) {
this.top = -1;
this.maxSize = maxSize;
stack = new Object[maxSize];
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return (top == -1);
}
public boolean isFull() {
return (top == maxSize -1);
}
public void push(Object item) {
if(this.isFull())
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
stack[++top] = item;
}
public Object peek() {
if(this.isEmpty())
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
return stack[top];
}
public Object pop() {
Object item = peek();
top--;
return item;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack st = new Stack(100);
st.push(1);
System.out.println(st.pop());
st.push(2);
st.push(3);
st.push(4);
System.out.println(st.pop());
System.out.println(st.pop());
System.out.println(st.pop());
System.out.println(st.top);
}
}
/*
1
4
3
2
-1
*/
- 연결리스트(LinkedList) 구현
public class Stack<T extends Comparable<T>> {
private Node head = null;
private class Node {
T item;
Node next;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return (head==null);
}
public void push(T item) {
Node oldHead = head;
head = new Node();
head.item = item;
head.next = oldHead;
}
public T pop() {
T item = peek();
head = head.next;
return item;
}
public T peek() {
if(isEmpty()) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
return head.item;
}
}
PREVIOUS[자료구조] 큐(Queue) in Java
